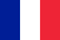
Osteochondrosis is a widespread disease of the spine, affecting the intervertebral discs and cartilage. Cervical and lumbar regions are more sensitive to such processes. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region can cause constant pain in the lumbar region and significantly complicate a person's life. Conservative methods are preferred in the treatment of the disease, surgical interventions are used only in extreme cases.
Causes of lumbar osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is not so much a disease, but a natural phenomenon that often occurs as a result of age-related degenerative changes in the spine. Normally, the disc in the lumbar region acts as a shock absorber between the two vertebrae and allows the joints and spine to move easily. The outer part of the disc, the annulus fibrosus, surrounds the soft inner core of the disc, the nucleus pulposus. Everyone's spinal discs undergo degenerative changes as they age, but not everyone develops symptoms.
Osteochondrosis is believed to begin with changes in the annulus fibrosus, intervertebral disc, and subchondral bone. The fibrous ring loses water, which reduces the spine's ability to withstand daily loads, misdistributing them. Overloading of the back of the spine causes arthritis of the facet joints and hypertrophy (growth, with the formation of osteophytes - bone growth) of the vertebral bodies adjacent to the affected disc.
Reference! According to statistics, 30% of people between the ages of 30 and 50 have some degree of degeneration of the spinal discs.
There are two main pathophysiological causes of pain in lumbar osteochondrosis. One possible cause of the pain is inflammation of the nerves as a result of the outer part of the disc rupturing and the inner core leaking out. Inflammatory proteins are released that irritate nerve tissue.
For the second reason, the vertebra, due to age-related deformation, can no longer effectively accept the load. This causes the spine to move abnormally and causes painful spasm of the back muscles that try to stabilize the spine.
The result of osteochondrosis can be the destruction of segments of the spine, causing radiculitis. Risk factors that trigger and accelerate degenerative processes in the spine are:
- hereditary tendency to diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- To smoke;
- Previous injuries;
- Hormonal and vascular disorders;
- Excessive body weight;
- Muscles that are too weak and do not provide the necessary support to the spine;
- Professional activities related to heavy physical labor (athletes, loaders).
Stages of development of lumbar osteochondrosis
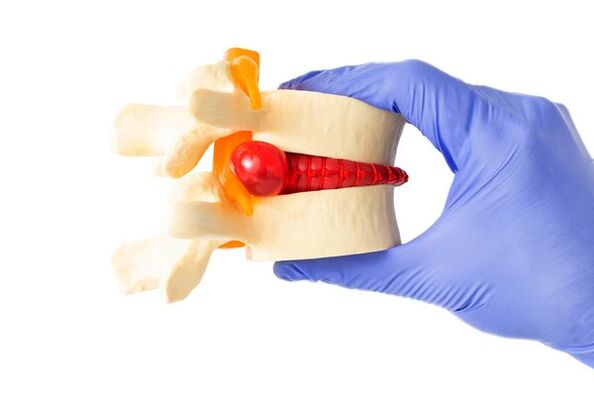
Disorders in the intervertebral discs, causing their degeneration and destruction, occur gradually. The entire pathological process goes through several stages, so the stages (or degrees) of lumbar osteochondrosis are distinguished:
- The first stage (degree) is characterized by mild symptoms. Painful sensations develop against the background of irritation of nerve endings by the nucleus pulposus, which penetrates into the fissures of the fibrous ring.
- The second stage is characterized by the displacement of the upper vertebra relative to the lower one due to the cracking of the nucleus and ring. These pathological processes, in addition to pain during movement, cause neurological symptoms, numbness and instability of the affected area.
- The third stage is characterized by increased pain and the appearance of ruptured intervertebral discs due to the violation of the integrity of the fibrous ring. Pain, sensory disturbances, and muscle weakness interfere with daily activities. Due to compression of the nerve roots, the activity of the urinary and intestinal systems may be disturbed.
- The fourth stage corresponds to the complete destruction of the intervertebral discs, they become fibrotic, and osteochondral growths of the vertebral bodies cause immobility of the spine in this section.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Get expert advice to get started:
- Neurologist
- Orthopedist
- Therapist
The main symptom of lumbar and sacral osteochondrosis is pain. It usually gets worse when sitting or twisting for a long time, bending the spine, or lifting a load. The pain may spread to the legs and groin and may be accompanied by numbness and weakness. Moderate, aching, dull pain, may be accompanied by attacks of exacerbation.
Symptoms directly depend on the stage of development of the pathology:
- In the early period, when degenerative changes are just beginning to appear, the symptoms are minimal.
- The intermediate stage, characterized by the weakening of the fibrous ring, can already manifest itself as back pain.
- At a later stage, when fibrosis develops in the structures and osteophytes form, the pain is less pronounced, but the mobility of the spine is significantly reduced.
The sensitivity of the lower back can be increased when touched. Characteristic shooting pains and tingling sensation in the hips and thighs are symptoms of compressed nerve roots caused by degenerative changes in the disc. Patients with lumbar osteochondrosis have difficulty bending forward, backward and sideways. Osteochondrosis can be complicated by the narrowing of the spinal canal accompanied by herniated discs and the appearance of additional symptoms.
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis

Making a diagnosis begins with taking an anamnesis, interviewing and examining the patient. The specialist will be interested in your complaints, physical activity, presence of old injuries, bad habits, illness in close relatives. During the physical examination, the doctor palpates (feels) the lower part of the spine, looking for tender areas, inflammation, or any abnormalities. He may also check sensation and perform motor tests.
The most popular method for diagnosing lumbar osteochondrosis is X-ray examination. When gas bubbles are detected in the thickness of the disc, the image will show the presence of osteophytes, narrowing of the disc joint space or the so-called "vacuum" symptom. Other methods used are:
- MRI, showing hydration (degree of water saturation), disc shape, height, allows identification of compressed nerves.
- CT scan, which allows you to study the condition of tissues in detail and diagnose disorders in the earliest stages.
- Invasive discography is used to locate the affected disc.
Reference! MRI is a fairly accurate diagnostic method, but it cannot detect rupture of the outer rings of the disc.
Methods of treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
The preferred treatment for lumbar degenerative disc disease associated with chronic pain is conservative treatment with physical therapy, exercise, and medication. It is recommended for patients with lumbar osteochondrosis:
- A daily regimen that includes sufficient rest and adequate physical activity;
- Regular physical exercises aimed at strengthening muscles;
- Nutritional analysis and lifestyle adjustments including weight loss.
Physiotherapy

Various physiotherapeutic methods have been successfully used to reduce back pain. Physiotherapy promotes regenerative processes in the disc, stimulates metabolic and transport processes, prevents the formation of adhesions and further damage.
Physiotherapy methods used in the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis include:
- Electrical stimulation. Electrical impulses help relieve back pain and improve blood circulation in the affected spine.
- Ultrasound therapy. Ultrasound waves can penetrate deep layers of tissue and help relieve inflammation and pain.
- Magnetotherapy. Magnetic fields can improve blood circulation and metabolic processes in tissues and promote their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Laser beams can help relieve pain, stimulate blood circulation, and stimulate tissue regeneration.
- Ultraphonophoresis. This method combines ultrasound therapy with the use of drugs that penetrate deep layers of tissue and help relieve inflammation and pain.
It is important! Contrary to popular belief, osteochondrosis can and should be treated. Without treatment, it will become a source of chronic pain and can cause numerous problems, including internal organ dysfunction.
Drug treatment
Analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to patients to relieve pain that interferes with daily activities. According to the indications, the doctor can prescribe stronger drugs: muscle relaxants, steroids and narcotic pain relievers. To relieve severe pain, therapeutic blockades are performed together with local anesthetics and glucocorticoids.
Surgery
Less often surgical intervention is used for osteochondrosis of the lumbar region. This may include disc arthroplasty or lumbar fusion (making it possible to fuse two vertebrae together, reducing pain by eliminating movement in this part of the spine).
If the movement of the spine is significantly impaired, special intervertebral spaces can be installed. In patients who do not respond to all other treatments, a total lumbar disc replacement may be performed.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis at home
The most effective thing you can do at home to maintain functionality and control pain is exercise. They will increase the flow of blood, oxygen and nutrients to the spine, helping to moisturize the cartilage and keep the spine flexible for as long as possible. In addition, exercise releases endorphins, which are natural pain relievers.
Frequent position changes also bring comfort. Some poses help to cope with the pain attack: kneeling, lying down, lying down. A short rest is necessary and beneficial, but prolonged bed rest only worsens the condition. Staying active is important to prevent disease progression. Patients with lumbar osteochondrosis benefit from walking, swimming, bicycling, yoga, Pilates, stretching, and muscle corset strengthening. The following measures also help:
- Applying heat to the lower back improves blood circulation and relieves muscle spasms and tension.
- Ice packs will help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Massage also relaxes muscles, relieves spasms and reduces pressure on the spine, thereby relieving pain. By increasing blood circulation in this area, metabolic processes improve and tissues are enriched with oxygen.
- Use of orthopedic mattresses and pillows. They will help maintain the correct position of the spine during sleep.
- Correct distribution of the load on the spine. When lifting heavy objects, you must use proper lifting technique to avoid straining the spine.
- Proper nutrition. A balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamins will help keep bones and joints healthy.
However, if there is pain or other symptoms, before starting the treatment of osteochondrosis at home, you should consult your doctor to get more accurate recommendations and assess the condition of the spine.
Which doctor should I see for lumbar osteochondrosis?
If symptoms characteristic of lumbar osteochondrosis appear, it is recommended to consult a neurologist or orthopedic doctor. If you have back pain, you can also make an appointment with a therapist. He will prescribe the necessary tests to make a diagnosis and refer to a specialist.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
Specialists of the nearest clinic in your city or another area are ready to understand the reasons and help you overcome the pain. Doctors usually have extensive clinical experience and master all modern methods of treatment and diagnosis of osteochondrosis in women and men. In most cases, a convenient location, excellent equipment and versatility of facilities are the priority of modern medicine, which allows to quickly pass any examination and restore the health of the musculoskeletal system. You can make an appointment on the website by calling the clinic that suits you, as well as by filling out an online form.
Prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis
Effective ways to prevent lumbar osteochondrosis are:
- Regular physical activity. Keep in good physical shape. Strengthen your back muscles. Back stretching and strengthening exercises will help keep your spine healthy.
- Reduce stress on the spine: Avoid unnecessary stress on the spine. Use proper lifting technique when lifting heavy objects.
- Posture correction: ensure proper posture. Sit and stand straight, do not slouch. To maintain the correct position of the spine during rest, choose an orthopedic pillow and mattress for sleeping. Buy quality shoes with good cushioning and support.
- If you have to sit for a long time due to the characteristics of your profession, pay attention to back support using orthopedic chairs. Avoid staying in one position for a long time. Take regular breaks and stretch your spine.
- Watch your weight. Excess weight can put extra stress on the spine.
- Avoid uncontrolled movements and back injuries. Be careful when doing sports or physical activity.
- Quit smoking, which can negatively affect your spine health.
By following simple recommendations, you can lead an active and full life, minimizing the risks of back pain. If you already have symptoms, lower back pain, be sure to see a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.